Size-Fractionated Microbiome Analysis — Day 4: Gene Catalog Construction & Functional Annotation
🌊 Size-Fractionated Microbiome Analysis — Day 4
In Day 1, we focused on metagenome preprocessing, in Day 1, we explored taxonomic profiling using Kaiju, and in Day 3, we conducted species-level profiling with mOTUs.
Today, in Day 4, I introduce gene catalog construction—a critical foundation for functional profiling of microbial communities.
This approach enables downstream analyses of substrate uptake transporters (ABC transporters, TonB-dependent receptors), CAZymes, and other functional genes. By building a unified, non-redundant gene catalog from metagenomes, we can map both DNA (metagenome) and RNA (metatranscriptome) reads to quantify functional potential and expression.
🧬 Why Build a Gene Catalog?
Traditional approach: Annotate each metagenome assembly independently
- Results in redundant gene sets across samples
- Difficult to compare gene presence/absence across communities
- Inflates computational costs for downstream analyses
Gene catalog approach:
- Pool all assembled genes from all metagenomes
- Cluster at high identity (e.g., 90%) to create a non-redundant reference
- Annotate once with functional databases
- Map reads from all samples (MG + MT) to the same catalog
- Enables direct comparison of functional potential (DNA) vs expression (RNA)
This workflow follows the methodology described in metagenomic studies for constructing prokaryotic gene catalogs.
🛠️ Workflow Overview
Metagenome Assemblies
↓
Prodigal (gene prediction)
↓
Concatenate all genes
↓
CD-HIT (90% clustering)
↓
Non-redundant Gene Catalog
↓
Prodigal (protein prediction on catalog)
↓
eggNOG-mapper (functional annotation)
↓
Annotated Gene Catalog
📁 Step 0: Project Directory Setup
First, create an organized directory structure:
cd /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23
mkdir -p substrate_FRed/{00_logs,01_catalog,02_mapping_MG,03_mapping_MT,04_counts,05_eggnog,06_function_sets,07_FRed}
Directory purposes:
-
00_logs/— SLURM job outputs and error logs -
01_catalog/— Gene prediction and catalog files -
02_mapping_MG/— Metagenome read mappings -
03_mapping_MT/— Metatranscriptome read mappings -
04_counts/— Gene abundance tables -
05_eggnog/— Functional annotations -
06_function_sets/— Substrate-specific gene sets -
07_FRed/— Functional redundancy analyses
🧪 Step 1: Gene Prediction from Metagenome Assemblies
Tool: Prodigal v2.6.3 (metagenome mode)
Prodigal identifies open reading frames (ORFs) and predicts protein-coding genes from assembled contigs.
1A. Predict genes from individual assemblies
Input: Individual metagenome assemblies (contigs ≥200 bp)
Output: .fna (nucleotide), .faa (protein), .gff (annotations)
SLURM batch script:
cat > 01_prodigal_MGs.sh <<'EOF'
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=prodigal_MGs
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=4
#SBATCH --mem=16G
#SBATCH --time=24:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=camplab
#SBATCH --array=1-N # Replace N with number of samples
#SBATCH -o /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/prodigal_MG_%A_%a.out
#SBATCH -e /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/prodigal_MG_%A_%a.err
module load prodigal/2.6.3
# Get sample name from array
SAMPLE_LIST="/project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/01_catalog/mg_assembly_list.txt"
SAMPLE=$(sed -n "${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}p" ${SAMPLE_LIST})
ASSEMBLY_DIR="/project/bcampb7/camplab/0_Raw_Data/Metagenome_estury/Assembly_All/MGs"
OUT_DIR="/project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/01_catalog/prodigal_MGs/${SAMPLE}"
mkdir -p ${OUT_DIR}
prodigal \
-i ${ASSEMBLY_DIR}/${SAMPLE}/final.contigs.fa \
-a ${OUT_DIR}/${SAMPLE}.faa \
-d ${OUT_DIR}/${SAMPLE}.fna \
-f gff \
-o ${OUT_DIR}/${SAMPLE}.gff \
-p meta
echo "Prodigal complete for ${SAMPLE}"
EOF
Key parameters:
-
-p meta— Metagenome mode (handles mixed community gene models) -
-a— Amino acid (protein) output -
-d— Nucleotide (gene) output -
-f gff— Gene feature format for downstream tools
Submit the job:
sbatch 01_prodigal_MGs.slurm
1B. Concatenate all predicted genes
After all Prodigal jobs complete, combine genes from all samples:
cd /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/01_catalog
cat prodigal_MGs/*/*.fna > all_MG_genes.fna
# Check total gene count
grep -c "^>" all_MG_genes.fna
In my case:
- Total genes before clustering: 67,609,507
🔗 Step 2: Non-Redundant Gene Catalog Construction with CD-HIT
Tool: CD-HIT-EST v4.8.1
CD-HIT clusters highly similar sequences to create a non-redundant gene set. This step removes redundancy across samples while preserving gene diversity.
2A. Cluster genes at 90% identity
SLURM script:
cat > 02_cdhit_catalog90.sh <<'EOF'
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=catalog90
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=32
#SBATCH --mem=200G
#SBATCH --time=48:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=camplab
#SBATCH -o /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/catalog90_%j.out
#SBATCH -e /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/catalog90_%j.err
# Load CD-HIT module or activate conda environment
# module load cd-hit/4.8.1
IN="/project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/01_catalog"
OUT="${IN}"
cd-hit-est \
-i ${IN}/all_MG_genes.fna \
-o ${OUT}/MG_gene_catalog90.fna \
-c 0.90 \
-n 8 \
-G 0 \
-aS 0.90 \
-T 32 \
-M 0
echo "CD-HIT clustering complete"
EOF
sbatch 02_cdhit_catalog90.slurm
Key parameters:
-
-c 0.90— 90% sequence identity threshold -
-n 8— Word size (optimized for 90% identity) -
-G 0— Global sequence identity (not local alignment) -
-aS 0.90— Alignment coverage for shorter sequence (90%) -
-T 32— Threads -
-M 0— Use all available memory
2B. Verify clustering results
cd /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/01_catalog
# Original genes
echo "Original genes:"
grep -c "^>" all_MG_genes.fna
# Non-redundant catalog
echo "Non-redundant catalog (90%):"
grep -c "^>" MG_gene_catalog90.fna
# Cluster information
wc -l MG_gene_catalog90.fna.clstr
My results:
- Original genes: 67,609,507
- Non-redundant catalog: 40,619,901
- Redundancy removed: ~40% (27 million redundant genes)
🧬 Step 3: Protein Prediction on Non-Redundant Catalog
Since CD-HIT operates on nucleotide sequences, we need to predict proteins from the clustered gene catalog for functional annotation.
SLURM script:
cat > 03_prodigal_catalog.sh <<'EOF'
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=prodigal_catalog
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=4
#SBATCH --mem=32G
#SBATCH --time=6:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=camplab
#SBATCH -o /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/prodigal_catalog_%j.out
#SBATCH -e /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/prodigal_catalog_%j.err
module load prodigal/2.6.3
cd /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/01_catalog
prodigal \
-i MG_gene_catalog90.fna \
-a MG_gene_catalog90.faa \
-d MG_gene_catalog90.genes.fna \
-f gff \
-o MG_gene_catalog90.gff \
-p meta
echo "Prodigal complete on gene catalog"
EOF
sbatch 03_prodigal_catalog.slurm
Output files:
-
MG_gene_catalog90.faa— Protein sequences (for eggNOG) -
MG_gene_catalog90.genes.fna— CDS nucleotide sequences -
MG_gene_catalog90.gff— Gene annotations
📊 Step 4: Functional Annotation with eggNOG-mapper
Tool: eggNOG-mapper v2.1+
eggNOG-mapper assigns functional annotations by mapping proteins to the eggNOG database, which integrates:
- KEGG Orthology (KO)
- COG/NOG functional categories
- Gene Ontology (GO)
- EC numbers
- KEGG pathways
4A. Download eggNOG database (one-time setup)
# Set database directory
export EGGNOG_DATA_DIR=/project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/databases/eggnog
# Download database
download_eggnog_data.py --data_dir ${EGGNOG_DATA_DIR}
4B. Run eggNOG-mapper on the catalog
SLURM script:
cat > 01_eggnog_catalog.sh <<'EOF'
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=eggnog_catalog
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=32
#SBATCH --mem=100G
#SBATCH --time=48:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=camplab
#SBATCH -o /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/eggnog_catalog_%j.out
#SBATCH -e /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/00_logs/eggnog_catalog_%j.err
export EGGNOG_DATA_DIR=/project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/databases/eggnog
# Load eggnog-mapper module or activate conda environment
# module load eggnog-mapper
# conda activate eggnog_env
OUTDIR="/project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/05_eggnog"
mkdir -p ${OUTDIR}
emapper.py \
-i /project/bcampb7/camplab/AL_JJ_oct23/substrate_FRed/01_catalog/MG_gene_catalog90.faa \
--itype proteins \
-o ${OUTDIR}/MG_catalog \
--output_dir ${OUTDIR} \
--cpu 32 \
--data_dir ${EGGNOG_DATA_DIR}
echo "eggNOG annotation complete"
EOF
sbatch 01_eggnog_catalog.slurm
Expected output:
-
MG_catalog.emapper.annotations— Main annotation table -
MG_catalog.emapper.seed_orthologs— Ortholog assignments -
MG_catalog.emapper.hits— DIAMOND search results
Runtime note: With ~40M proteins, eggNOG annotation may take 24-48+ hours.
🔍 Step 5: Extracting Substrate Uptake Genes
After eggNOG annotation completes, we’ll extract specific functional gene categories:
- ABC transporters — Substrate-specific import systems
- TonB-dependent receptors (TBDTs) — Outer membrane transporters
- CAZymes — Carbohydrate-active enzymes
Parsing strategy (to be implemented):
# Extract ABC transporters
grep -i "ABC transporter" MG_catalog.emapper.annotations > ABC_transporters.tsv
# Extract TBDTs
grep -i "TonB.*receptor" MG_catalog.emapper.annotations > TBDTs.tsv
# Further substrate assignment based on eggNOG/KEGG annotations
This step will be detailed in Day 5 when we focus on functional categorization and substrate specificity.
📈 Next Steps (Day 5 Preview)
With the annotated gene catalog complete, the next steps include:
- Read mapping — Map MG and MT reads to the catalog using Bowtie2
- Gene abundance quantification — Calculate TPM/RPKM values
- Functional categorization — Assign substrate specificity to transporters
- Functional redundancy (FRed) — Compare PA vs FL communities
- RNA/DNA ratios — Identify actively expressed vs dormant functions
✅ Summary of Day 4
| Step | Tool | Input | Output | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene prediction | Prodigal | Assemblies | Gene sequences (.fna, .faa) | Identify ORFs |
| Concatenation | bash | All genes | Combined FASTA | Pool genes |
| Clustering | CD-HIT | All genes | Non-redundant catalog (90%) | Remove redundancy |
| Protein prediction | Prodigal | Catalog genes | Protein sequences (.faa) | Prepare for annotation |
| Functional annotation | eggNOG-mapper | Catalog proteins | Annotated genes | Assign functions |
Key achievements:
- Built a 40.6 million non-redundant gene catalog from 67.6 million raw genes
- Removed ~40% redundancy across samples
- Created a unified reference for functional profiling
- Annotated genes with KEGG, COG, and GO terms
🔗 Resources
- Prodigal documentation: https://github.com/hyattpd/Prodigal
- CD-HIT user guide: http://weizhong-lab.ucsd.edu/cd-hit/
- eggNOG-mapper: http://eggnog-mapper.embl.de/
- KEGG database: https://www.genome.jp/kegg/
📂 Repository Structure
Please visit : https://github.com/jojyjohn28/Size_Fractionated_Microbiome_Analysis
day04_gene_catalog/
├── README.md # Workflow overview
├── NOTES.md # Analysis notes and troubleshooting
├── scripts/
├── 01_prodigal_MGs.sh
├── 02_cdhit_catalog90.sh
├── 03_prodigal_catalog.sh
└── 01_eggnog_catalog.sh
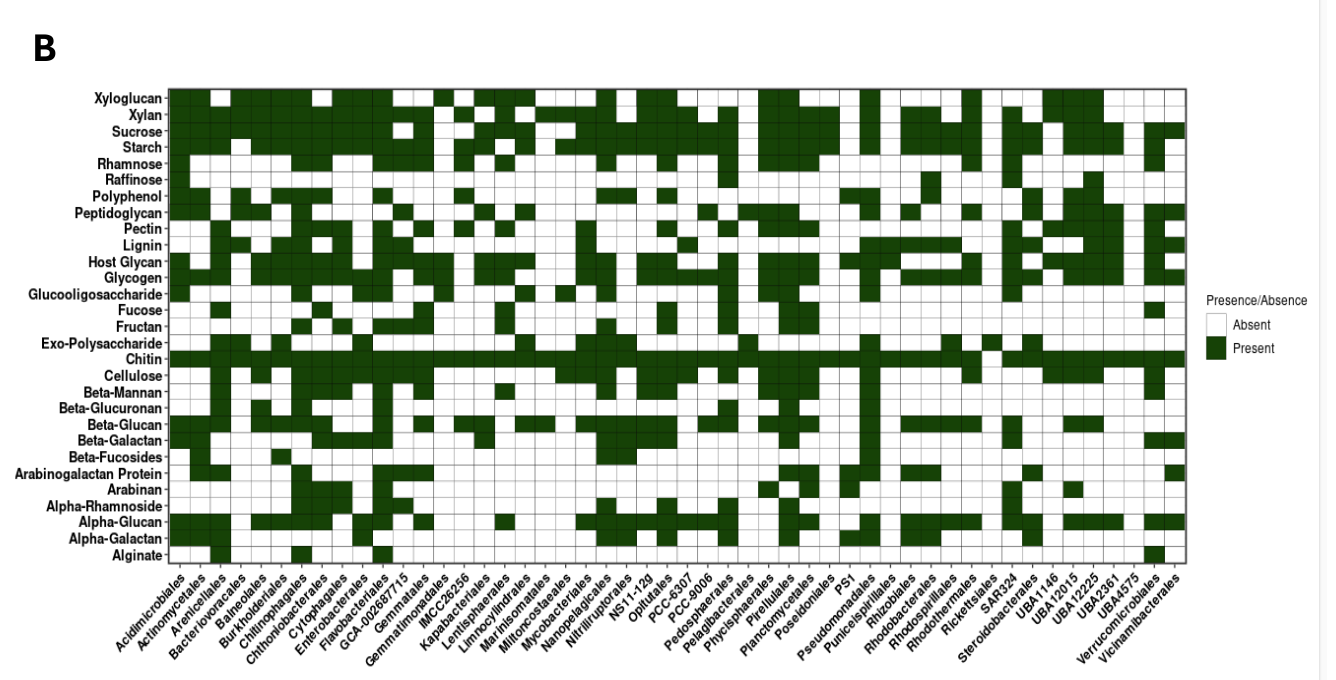
As my aim is to find the resouce partitioning the image showing different substrte uptake pattern by order in the metagnome. This is a draft picture.
Stay tuned for Day 5, where we’ll map reads to the catalog and begin quantifying functional gene expression!
Questions? Comment below or reach out.