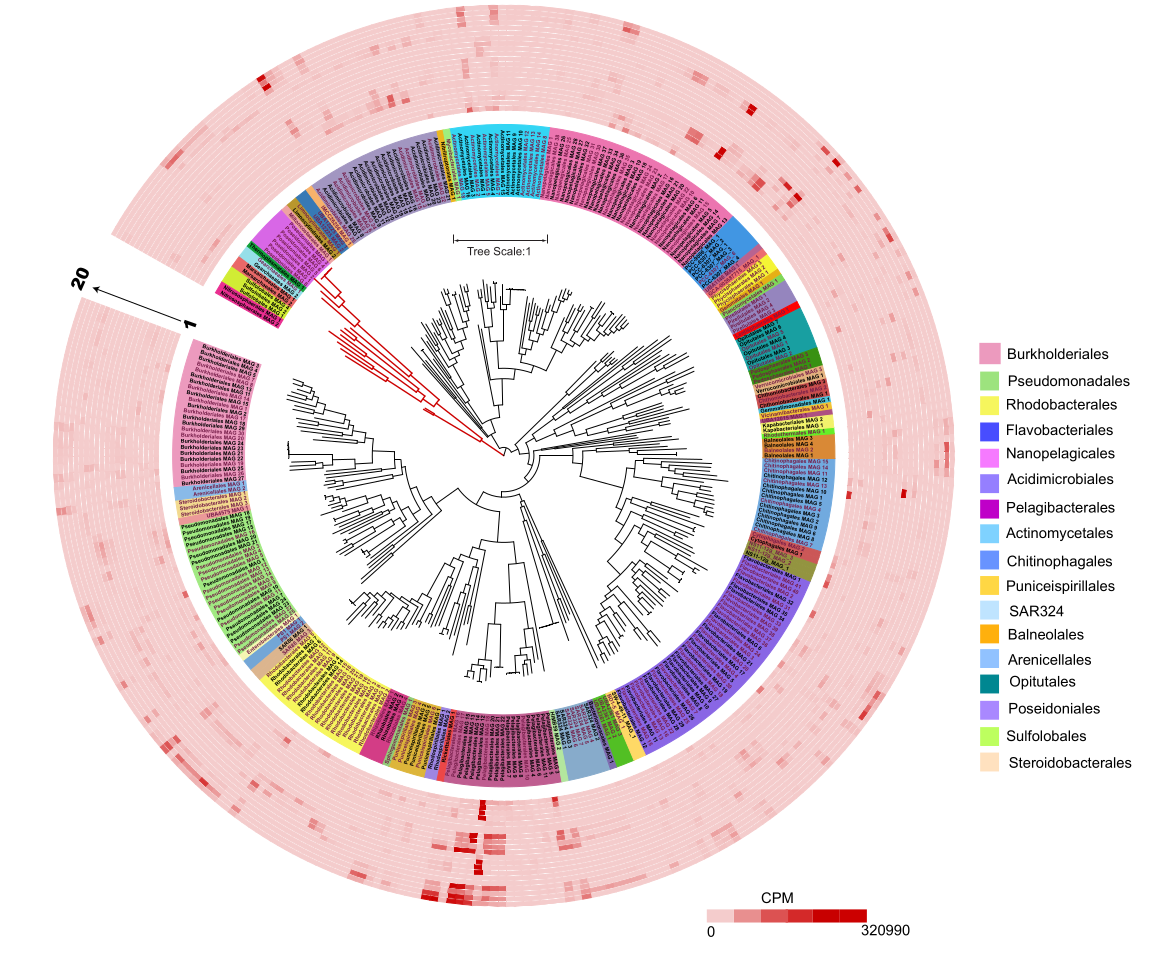
GTDB-Tk Complete Workflow
When I began in bioinformatics, those beautifully annotated phylogenetic trees felt impossible to create. Later, when I started binning and whole-genome analysis, visualizing my own genomes with that same level of detail became one of my top goals.
That’s when I finally ended up using GTDB-Tk for tree building and iTOL for annotation, and it opened a whole new world of possibilities.
Introduction
GTDB-Tk (Genome Taxonomy Database Toolkit) has become one of the most widely used tools for classifying bacterial and archaeal genomes using the GTDB standard taxonomy.
In this blog post, I walk through a complete, reproducible workflow:
✔ Installing GTDB-Tk
✔ Setting up a conda environment
✔ Downloading the GTDB reference database
✔ Running identify, align, and classify
✔ Handling common errors like MASH DB
✔ Running the full de_novo_wf
✔ Exporting the final tree to iTOL
✔ A short intro to iTOL annotations
All commands are based on my workflows on the Palmetto HPC Cluster.
1. Creating & Activating GTDB-Tk Conda Environment
If you don’t already have GTDB-Tk installed, create a fresh environment:
conda create -n gtdbtk_env -c bioconda -c conda-forge gtdbtk
Or install it in a custom project folder: You may need little more storage to set up the updated database
conda create -p path/to/desired/folder -c bioconda -c conda-forge gtdbtk
Activate and Verify installation:
gtdbtk --version
2. Downloading the GTDB Reference Database
GTDB-Tk requires the full reference database (e.g., release R207, R214, etc.). Download from: 👉 https://data.gtdb.ecogenomic.org/ Example (Bacteria + Archaea): Keep in mind this is almost more than 100 GB;
wget https://data.gtdb.ecogenomic.org/releases/release214/214.1/gtdbtk/gtdbtk_r214_data.tar.gz
Extract and set environment variable
tar -xzf gtdbtk_r214_data.tar.gz -C /project/bcampb7/camplab/databases/
export GTDBTK_DATA_PATH=/project/bcampb7/camplab/databases/gtdbtk_r214_data #or run line below
echo "export GTDBTK_DATA_PATH=/project/bcampb7/camplab/databases/gtdbtk_r214_data" >> ~/.bashrc #to make it permanant
gtdbtk check_install
3. GTDB-Tk Workflow (Identify → Align → Classify)
Now we run GTDB-Tk on your genomes. 3.1 Identify Marker Genes
gtdbtk identify \
--genome_dir path/to/directory/with/genomes \
--out_dir path/to/output/gtdbtk/identify \
--extension fa \
--cpus 32 #change accordingly
#change according to your genome.extension; fa or fasta
3.2 Align Marker Genes
gtdbtk align \
--identify_dir path_to/gtdbtk/identify \
--out_dir path_for/gtdbtk/align \
--cpus 32
3.3 Classify Genomes
gtdbtk classify \
--genome_dir path \
--align_dir /path/align \
--out_dir /path/classify \
-x fasta \
--cpus 32 \
--mash_db path_for_saving_db
4. Running the Full de_novo_wf (Automatic Tree Building)
This workflow performs everything: identify → alignment → tree → taxonomy.
gtdbtk de_novo_wf \
--genome_dir /project/dkarig/ecocoat/NCBI_oct22/need_biosamples/missing_assemblies_all \
--out_dir /project/dkarig/ecocoat/NCBI_oct22/need_biosamples/missing_assemblies_all/gtdbtk \
--extension fa \
--bacteria \
--cpus 32 \
--outgroup_taxon p__Chloroflexota \
--skip_gtdb_refs \
--custom_taxonomy_file /scratch/jojyj/UK/Genomes/gtdbtk/custom_taxonomy_file.tsv
Notes:
● Outgroup: Choose a phylum not present in your samples based on the sample type. I used Chloroflexota for my esturine MAGs. But for soil it is not correct.
● –skip_gtdb_refs: reduces tree size by removing thousands of reference genomes.
● Custom taxonomy file: generated in classify output → you can edit to customize clade names.
Output tree (important file):
gtdbtk.bac120.decorated.tree
5. Converting GTDB-Tk Tree For iTOL
gtdbtk convert_to_itol \
--input_tree /scratch/jojyj/UK/Genomes/gtdbtk/de_novo/gtdbtk.bac120.decorated.tree \
--output_tree /scratch/jojyj/UK/Genomes/gtdbtk/de_novo/OUTPUT_TREE
This creates:
OUTPUT_TREE.tree
OUTPUT_TREE.metadata.tsv
Upload OUTPUT_TREE.tree to iTOL. 👉 https://itol.embl.de/
6. Quick Start Guide to iTOL
iTOL (Interactive Tree of Life) is one of the best online tree-visualization tools.
What you can do in iTOL
● Upload trees (Newick format)
● Add colors for taxonomy (phylum, genus, species)
● Add heatmaps (genome size, CAZymes, AMGs, completeness)
● Add data strips (free-living vs particle-attached, salinity, depth)
● Collapse clades
● Export high-resolution images (SVG, PNG, PDF)
Quick annotation starter files
● colors.txt → Color by clades
● metadata_strip.txt → Add sample categories (Bay, Season, Salinity)
● metadata_heatmap.txt → Add numeric values (gene counts, FRed)
7. Summary
By combining GTDB-Tk + iTOL, you can go from raw genomes to:
✔ GTDB-consistent taxonomy ✔ High-quality phylogenomic alignment ✔ Beautiful publication-ready trees ✔ Metadata-rich visualization
This pipeline is essential for MAG studies, isolate genomes, and comparative genomics.